Often called a stiff or “frozen shoulder,” adhesive capsulitis occurs in about 2% to 5% of the general population. It affects women more than men and typically occurs in people who are over the age of 45. Of the people who have had adhesive capsulitis in one shoulder, 20% to 30% will get it in the other shoulder.
Adhesive capsulitis is the stiffening of the shoulder due to scar tissue, which results in painful movement and loss of motion. The actual cause of adhesive capsulitis is a matter for debate. Some believe it is caused by inflammation, such as when the lining of a joint becomes inflamed (synovitis), or by autoimmune reactions, where the body launches an “attack” against its own substances and tissues. Other possible causes include:
- Reactions after an injury or surgery
- Pain from other conditions—such as arthritis, a rotator cuff tear, bursitis, or tendinitis—that has caused you to stop moving your shoulder
- Immobilization of your arm, such as in a sling, after surgery or fracture
Often, however, there is no known reason why adhesive capsulitis starts.
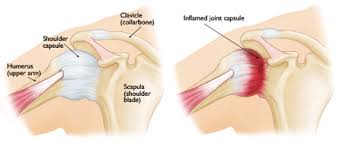
Most people with adhesive capsulitis have worsening pain and then a loss of range of movement. Adhesive capsulitis can be broken down into 4 stages, and your physical therapist can help determine what stage you are in and if therapy can help in the stage you are in at the time:
Stage 1 – “Pre-Freezing”
During this stage, it may be difficult to identify your problem as adhesive capsulitis. You’ve had symptoms for 1 to 3 months, and they’re getting worse. There is pain with active movement and passive motion (movements that a physical therapist does for you). The shoulder usually aches when you’re not using it, but pain increases and becomes “sharp” with movement. You’ll have a mild reduction in motion during this period, and you’ll protect the shoulder by using it less. The movement loss is most noticeable in “external rotation” (this is when you rotate your arm away from your body), but you might start to lose motion when you raise your arm (called “flexion and abduction”)or reach behind your back (called “internal rotation”). You’ll have pain during the day and at night.
Stage 2 – “Freezing”
By this stage, you’ve had symptoms for 3 to 9 months, most likely with a progressive loss of shoulder movement and an increase in pain (especially at night). The shoulder still has some range of movement, but this is limited by both pain and stiffness.
Stage 3 – “Frozen”
Your symptoms have persisted for 9 to 14 months, and you have greatly decreased range of shoulder movement. During the early part of this stage, there is still a substantial amount of pain. Toward the end of this stage, however, pain decreases, with the pain usually occurring only when you move your shoulder as far you can move it.
Stage 4 – “Thawing”
You’ve had symptoms for 12 to 15 months, and there is a big decrease in pain, especially at night. You still have a limited range of movement, but your ability to complete your daily activities involving overhead motion is improving at a rapid rate.

Often, physical therapists don’t see patients with adhesive capsulitis until well into the freezing phase or early in the frozen phase. Your physical therapist will perform a thorough evaluation, including an extensive health history, to rule out other diagnoses. Your therapist will look for a specific pattern in your decreased range of motion; it’s called a “capsular pattern” and is typical with adhesive capsulitis. In addition, your therapist will consider other conditions you might have—such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune disorders—that are associated with adhesive capsulitis.
Your physical therapist’s overall goal is to restore your movement so that you can perform your activities and life roles. Once the evaluation process has identified the stage of your condition, your therapist will create an exercise program tailored to your needs. Exercise has been found to be most effective for those who are in stage 2 or higher.
